Did you know that 71% of users with disabilities leave a website immediately if it is not accessible? That is a massive segment of the market you might be ignoring. Understanding accessibility compliance is about more than avoiding lawsuits or checking boxes. It is about opening your digital and physical doors to everyone. This guide shows you how to protect your business and grow your customer base.
Quick Summary
Accessibility ensures people with disabilities can effectively use your products, services, and facilities. While laws like the Americans with Disabilities Act mandate this, it also significantly improves the user experience for all customers. Compliance encompasses digital spaces, such as websites, and physical locations, including storefronts. Start by conducting an audit to identify gaps, implement necessary changes, and mitigate your legal risks.
Why is accessibility compliance strategic?
Many business owners view regulations as red tape, but shifting your perspective reveals a powerful growth engine. When you remove barriers, you allow more people to engage with your brand.
The Business Value of Inclusion
Targeting the disability market is a smart financial move. The global market of people with disabilities controls over $13 trillion in disposable income. By prioritizing disability inclusion, you tap into this spending power.
- Brand Loyalty: Customers value socially responsible companies.
- Innovation: Solving problems related to low vision or mobility injuries often leads to better products for everyone.
- Risk Mitigation: Avoiding reputational damage from social media backlash is crucial.
- Better Service: Improving access is the ultimate form of customer service.
Defining Accessibility in a Business Context
Accessibility means ensuring that people with diverse abilities can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with your business. This concept applies to your physical headquarters and your digital services.
It involves considering how screen reader users navigate your site or how someone using voice controls interacts with your app. It also means ensuring service animals are welcomed in your public accommodations. Whether you are a local bakery or a SaaS startup, user experiences must be inclusive.
What are the legal frameworks?
Navigating the alphabet soup of regulations can be confusing, but understanding the core laws is essential for risk management and protecting your bottom line.
Understanding the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a federal civil rights law designed to protect people with disabilities from discrimination. It stands as the central framework for accessibility requirements in the United States.
- Title I: This covers employment. It obligates employers to make reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities who are qualified for their roles.
- Title II: This applies to state and local government services, such as transit agencies.
- Title III: This is critical for businesses. It mandates that public accommodations (like hotels, restaurants, and retail stores) be accessible.
- Title IV: Focuses on telecommunications.
- Title V: Contains miscellaneous provisions.
Courts and the Department of Justice increasingly interpret Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act to apply to websites, meaning that inaccessible company websites can lead to ADA compliance lawsuits.
To help businesses maintain compliance and reduce legal risk, platforms like Accessify can continuously monitor websites and identify potential accessibility violations. They provide actionable insights for remediation before these issues escalate into legal problems.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) explained
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines are technical standards developed by the Web Accessibility Initiative of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). They are not laws themselves, but rather benchmarks used in legal settlements and agreements.
- Perceivable: Information must be presentable to users in ways they can perceive (e.g., alt text for images).
- Operable: User interface components must be operable (e.g., keyboard navigation).
- Understandable: Information and operations must be clear.
- Robust: Content should be easily readable by assistive technologies without error.
Most legal precedents cite WCAG standards at Level AA as the target for digital accessibility.
Other Relevant Accessibility Standards
Depending on your location and industry, other accessibility standards may apply.
- Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act mandates accessibility for electronic and information technology used by federal agencies to support individuals with disabilities. This requirement often applies to contractors selling to the government.
- Section 504: Prohibits discrimination in programs that receive federal aid.
- State Laws: The California Assembly Bill 434 and California’s Unruh Civil Rights Act have strict requirements. New York’s accessibility laws are also stringent.
- International: If you sell globally, consider the European Accessibility Act, the Equality Act in the UK, the Canada Standard on Web Accessibility, and the Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act.
How to Build an Accessible Business?
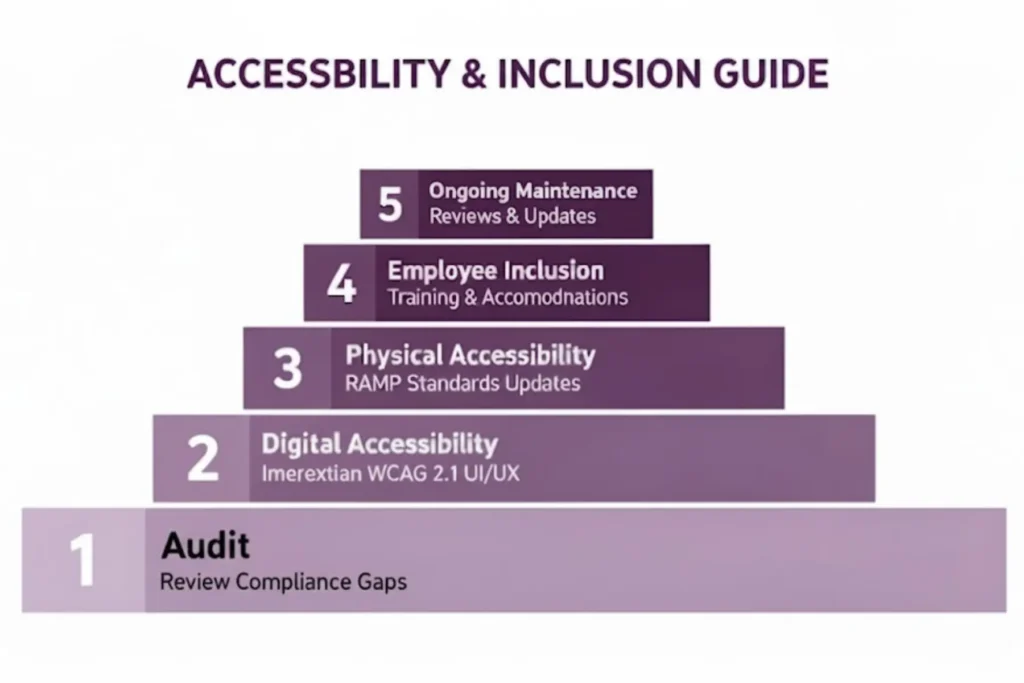
Moving from theory to action requires a systematic approach to both your physical and digital environments to ensure true accessibility compliance.
Conducting Accessibility Audits to Know Where You Stand
You cannot fix what you do not measure. Accessibility audits are the first step in your compliance journey.
- Run Automated Scans: Utilize an automated scanner or accessibility checker, such as the WAVE tool or IBM Equal Access Accessibility Checker. These catch about 30% of issues.
- Perform Manual Testing: A manual audit by experts is essential. They test user experience nuances that robots miss.
- Test with Assistive Tech: Have testers use a screen reader or adaptive keyboard to navigate your digital content.
- Physical Inspection: Walk through your physical space to identify accessible route issues and determine the need for barrier removal.
Traditional audit tools, such as WAVE, Axe, or manual checklists, catch only a portion of accessibility issues. Accessify provides continuous scanning and centralized issue tracking, helping businesses maintain compliance over time and prevent regressions as content and features change.
Digital Accessibility to Ensure an Inclusive Online Presence
Your website’s accessibility is your digital storefront. To meet accessibility requirements, focus on these core elements.
- Visuals: Add descriptive alt text to all images using the alt attribute. Ensure high color contrast and the correct contrast ratio for text.
- Navigation: Ensure keyboard-only navigation is possible. Users should see a visible focus indicator as they navigate through the content.
- Structure: Use semantic HTML and ARIA roles correctly to ensure that screen readers accurately understand the layout.
- Multimedia: Provide closed captions for video content and transcripts for audio. Accessible multimedia is non-negotiable.
Physical Accessibility to Create Welcoming Spaces
For brick-and-mortar businesses, ADA standards for accessible facilities are very specific.
- Parking: Ensure you have the correct number of van-accessible parking spaces.
- Entrances: Ramps and automatic doors provide access for individuals with mobility devices.
- Restrooms: Install grab bars and ensure sinks are at the correct height for use.
- Service Counters: Lower sections of counters are available for wheelchair users, or alternative input devices can be provided for payments.
Workplace Accessibility and Employee Inclusion
Workplace accessibility goes beyond the physical office. It includes your digital ecosystem and hiring practices.
- Recruiting: Ensure job applications and job application platforms are accessible to screen readers.
- Internal Tools: Employee software systems must be accessible and usable by all employees.
- Culture: Train staff on disability laws, such as the Disability Discrimination Act.
- Policies: Create clear procedures for requesting reasonable adjustments.
How to Sustain Accessibility Efforts?
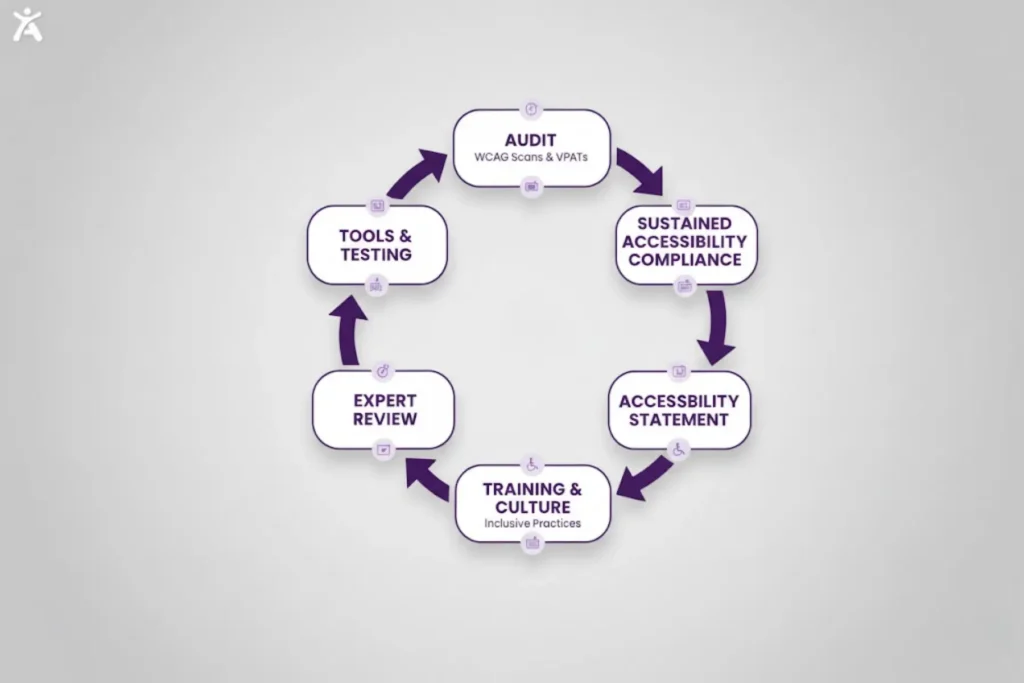
Compliance is not a one-time checklist but an ongoing commitment that evolves with technology and your business’s growth.
Leveraging Accessibility Tools and Technology
Technology can help maintain your standards. An accessibility widget can offer users temporary adjustments, such as contrast and text scaling, but it does not replace fixing the underlying code.
- Testing Tools: Integrate tools like Deque Axe into your development pipeline to enhance testing capabilities.
- CMS Plugins: Utilize plugins that prompt you for alternative text (alt text) before publishing.
- Captioning Services: Use automated tools for closed captioning but always review them for accuracy.
For businesses seeking continuous coverage and more effective issue management, Accessify complements these tools by providing ongoing scanning, centralized issue tracking, and actionable insights. These tools help teams maintain accessibility consistently over time without adding manual overhead.
Building an Accessibility-First Culture
To avoid legal risks, accessibility must be part of your company’s DNA, not an afterthought in digital marketing.
- Train your designers on contrast ratios and layout.
- Teach developers about Level AA success criteria.
- Educate content creators on writing in plain language and using camelCase for hashtags.
- Encourage customers to provide feedback on the mobile usability and accessibility of our services.
Creating an Accessibility Statement
An accessibility statement on your website shows your commitment. It should outline your target conformance levels (usually WCAG 2.1 AA) and provide a contact method for reporting issues. This transparency builds trust and can sometimes help mitigate legal risks.
When to Seek Expert Guidance
While automated scanners are helpful, they are not a silver bullet. If you receive a demand letter or are redesigning a complex site, consult an expert. Whether it is understanding Section 255 for telecom or FCC rules, professional advice is often more cost-effective than a lawsuit.
Conclusion:
Accessibility compliance is a journey, not a destination. By adhering to ADA regulations and WCAG standards, you protect your business from litigation while opening your arms to millions of potential customers. Whether you are fixing contrast errors or installing a ramp, every step matters. Start today and build a business that truly welcomes everyone.
FAQs
Adherence to accessibility standards ensures that websites and apps are usable by people with disabilities. It follows WCAG standards for perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust content, meeting legal requirements.
Businesses can audit pages using established tools like Axe or WAVE. Accessify also helps scan sites, highlight issues, and provide actionable insights to maintain ongoing accessibility standards efficiently.
Laws like the ADA often require adherence to accessibility standards for websites related to public services. Following WCAG standards reduces legal risk and ensures equal online participation for all users, keeping sites legally compliant.
Accessible design adherence improves navigation, readability, and structure for all users and search engines. It helps identify design gaps, supporting compliance while boosting engagement, reducing bounce, and enhancing ranking signals.
Begin with key page evaluations, address critical WCAG issues, and establish internal guidelines to ensure compliance. Tools like Axe, WAVE, or Accessify simplify audits, prioritize issues, and support efficient adherence to long-term accessibility standards.













